The pharmaceutical industry relies heavily on advanced laboratory equipment to ensure precision, sterility, and efficiency throughout the drug discovery, development, and production lifecycle. Each piece of equipment serves a specialized role:
Shaker incubators accelerate microbial and cell culture growth for protein and metabolite production.
Standard and CO₂ incubators support vital cell line maintenance and drug efficacy testing.
Biological safety cabinets ensure aseptic conditions for high-risk biological work.
Laminar flow benches provide sterile environments for safe handling of non-hazardous materials.
Bioreactors are indispensable for scaling up biologics and vaccines.
Chillers maintain thermal stability for sensitive instruments and processes.
Ultrasonic cell disruptors enable efficient extraction and formulation of therapeutic biomolecules.
1. Shaker Incubator
Function: Combines temperature-controlled incubation with orbital shaking for homogeneous mixing and oxygenation.
Pharmaceutical Applications:
Microbial fermentation: Cultivation of E. coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and other microbes for recombinant protein and enzyme production.
Plasmid preparation: Growing transformed bacteria before plasmid extraction.
Cell line development: Especially for suspension-adapted mammalian or insect cells (e.g., CHO, HEK293).
High-throughput screening: Drug candidates tested against microbes or cultured cells in 24-/96-/384-well plates with constant agitation.
Typical Users: R&D labs, bioprocess engineers, QC microbiology departments, CROs.

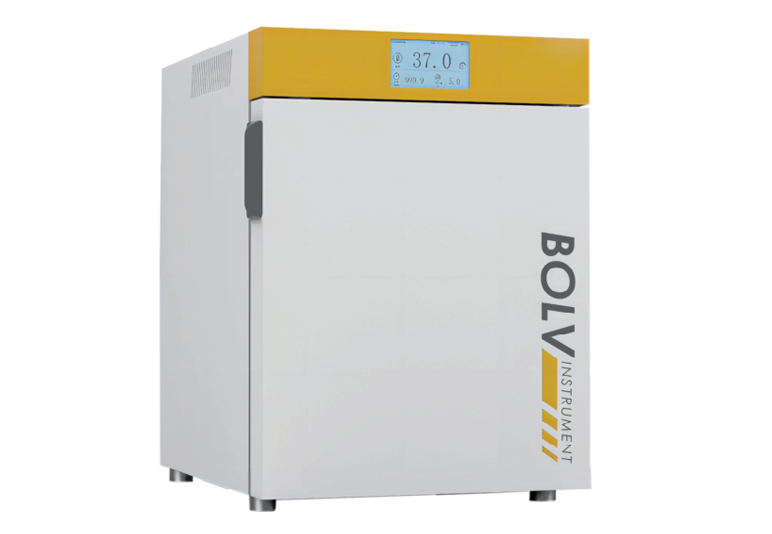
2. Incubator (Standard or CO₂)
Function: Maintains a controlled environment with precise temperature (and CO₂ concentration for CO₂ incubators).
Pharmaceutical Applications:
Cell and tissue culture: Culturing of adherent mammalian cell lines for vaccine or antibody development.
Drug efficacy and toxicity testing: Cultured cells used to test cytotoxic effects of compounds.
Stability testing: Incubation of formulations under controlled conditions to simulate long-term storage (ICH guidelines).
Viral propagation: Incubation of cells infected with virus strains for vaccine production.
Typical Users: Biotechnology companies, pharma QC/QA labs, virology labs.
3. Biological Safety Cabinet (BSC)-Class II
Function: Provides product, personnel, and environmental protection with HEPA-filtered airflow and negative pressure containment.
Pharmaceutical Applications:
Aseptic operations: Critical for working with sterile cell cultures, vaccine formulation, and contamination-sensitive operations.
Pathogen handling: Safe manipulation of infectious agents for diagnostics or therapeutic development.
Preparation of sterile injectables: Used in cleanroom environments for sterile compounding or fill-finish steps.
Typical Users: Biosafety labs, vaccine production plants, formulation labs.

4. Laminar Flow Bench (Horizontal or Vertical)
Function: Provides HEPA-filtered, particle-free airflow over the work area; protects samples from contamination but not the user.
Pharmaceutical Applications:
Media preparation: Pouring and aliquoting of sterile media for culture work.
QC sample preparation: For environmental monitoring or microbial assays.
Instrument setup: Calibration or assembly of clean lab devices under sterile conditions.
Typical Users: QC microbiology labs, compounding facilities, formulation rooms.

5. Bioreactor (Lab-Scale to Industrial)
Function: Allows controlled cultivation of biological systems with real-time monitoring and control of pH, DO, temperature, and agitation.
Pharmaceutical Applications:
Monoclonal antibody production: CHO cells grown in fed-batch or perfusion mode for biologics.
Vaccine production: Cultivation of viral or bacterial agents in host cells for inactivated/live vaccines.
Recombinant protein expression: Expression and harvest of therapeutic enzymes or hormones.
Biosimilar development: Scale-up and process optimization for generic biologics.
Typical Users: Biomanufacturing facilities, upstream bioprocessing teams, CDMOs.

6. Chiller / Recirculating Cooling System
Function: Provides constant, adjustable cooling for lab instruments and reactors.
Pharmaceutical Applications:
Fermentation process cooling: Maintains optimal bioreactor temperatures during exothermic microbial growth.
Solvent recovery: Used with rotary evaporators or distillation columns in formulation labs.
Equipment thermal stability: Maintains temperature for HPLC detectors, rotary evaporators, centrifuges, and lyophilizers.
Typical Users: Chemical synthesis labs, fermentation labs, API production sites.

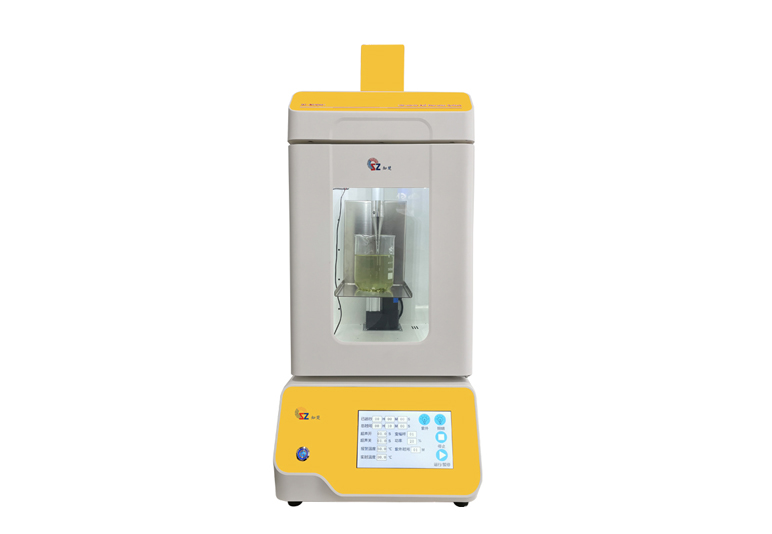
7. Ultrasonic Cell Disruptor
Function: Uses ultrasonic waves to create cavitation bubbles, disrupting cells and releasing intracellular components.
Pharmaceutical Applications:
Protein extraction: From bacterial, yeast, or mammalian cells for downstream purification.
DNA/RNA extraction: Disruption of cells or tissues for genomic or transcriptomic analysis.
Nanoparticle and liposome preparation: Helps in the formation of uniform drug delivery vesicles.
Emulsification and homogenization: For preparation of stable formulations like nanoemulsions or suspensions.
Typical Users: Analytical labs, formulation R&D, molecular biology labs.
 English
English
















